

It is an important look at the recommended weight bearing status for the injury. All patients with tibial shaft fractures should have ice applied to the injury and elevation of the extremity. Due to the circumferential nature of casts, even minimally displaced fractures treated in a cast may represent or worsen overnight A patient that presented with mild swelling may degrade overnight, therefore, it is vital for floor nurses to be aware whether these patients have increasing pain overnight. Compartment syndrome can develop in open and closed tibia fracture as well as before or after surgery.

Signs and symptoms of compartment syndrome are important for all members of the health care team to know. Antibiotic therapy can then continue into the postoperative period Bedside debridement of gross contamination is also necessary along with provisional splinting. From a triage standpoint, patients with open injuries or concern for compartment syndrome should undergo urgent evaluation.Įven prior to imaging, if there is visible bone or known open fracture, antibiotics should be started to help combat the risk of infection. A proper history, physical, and adequate imaging should take place promptly. Most patients with tibial shaft fractures will present to the emergency room. Location can be proximal, mid-shaft, or distal, or categorized based on the pattern - transverse, oblique, spiral, or comminuted. įractures can also be classified descriptively. This classification is used more for research purposes. There are other subclassifications of the AO/OTA classification system based on the location and presence of associated fibula fracture. The fracture is considered A-simple fracture, B-wedge fracture, C-complex. The tibial shaft denotes as bone segment 4.
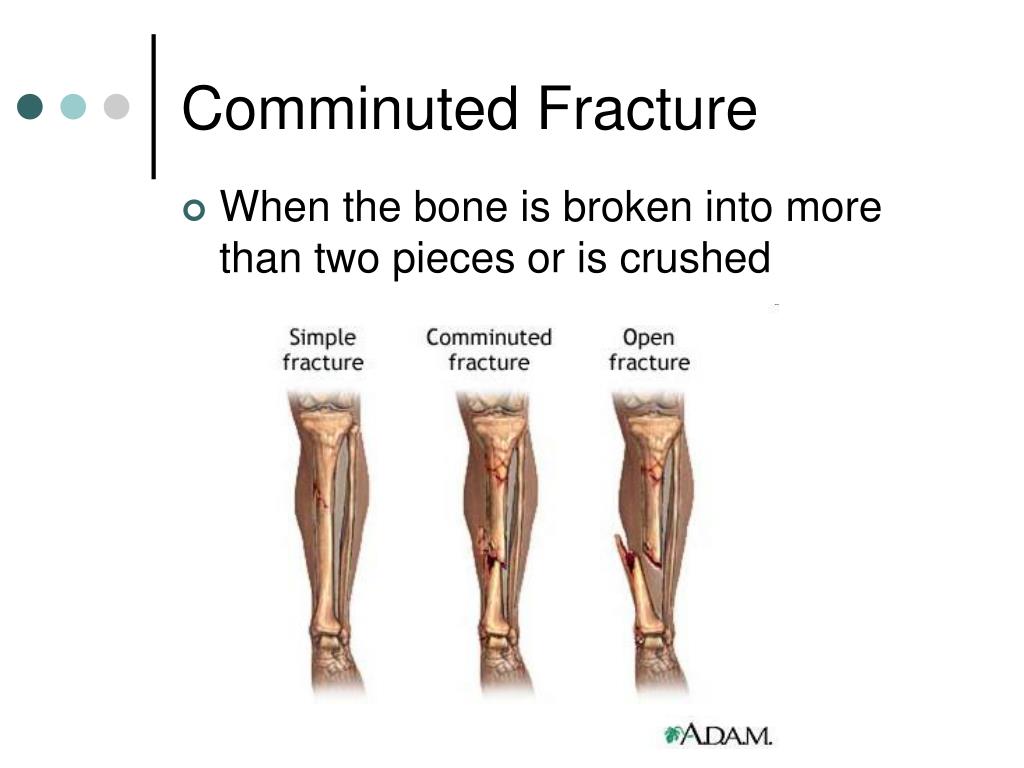
The tibia can be formally classified using the AO/OTA classification. Medical assessment for all surgical patients should include basic labs (CBC, BMP, and PT/INR are applicable) as well as a chest radiograph and EKG.Įlderly patients with diagnosed or suspected cardiac disease may benefit from preoperative cardiology evaluation. However, a CT scan is often used to assess intra-articular injuries that extend into the tibial plafond or plateau. Imaging: radiograph - AP and lateral of the tibia, recommend imaging the joint above and below of the knee and ankle.ĬT scans are not needed routinely on tibial shaft fractures.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
